Introduction
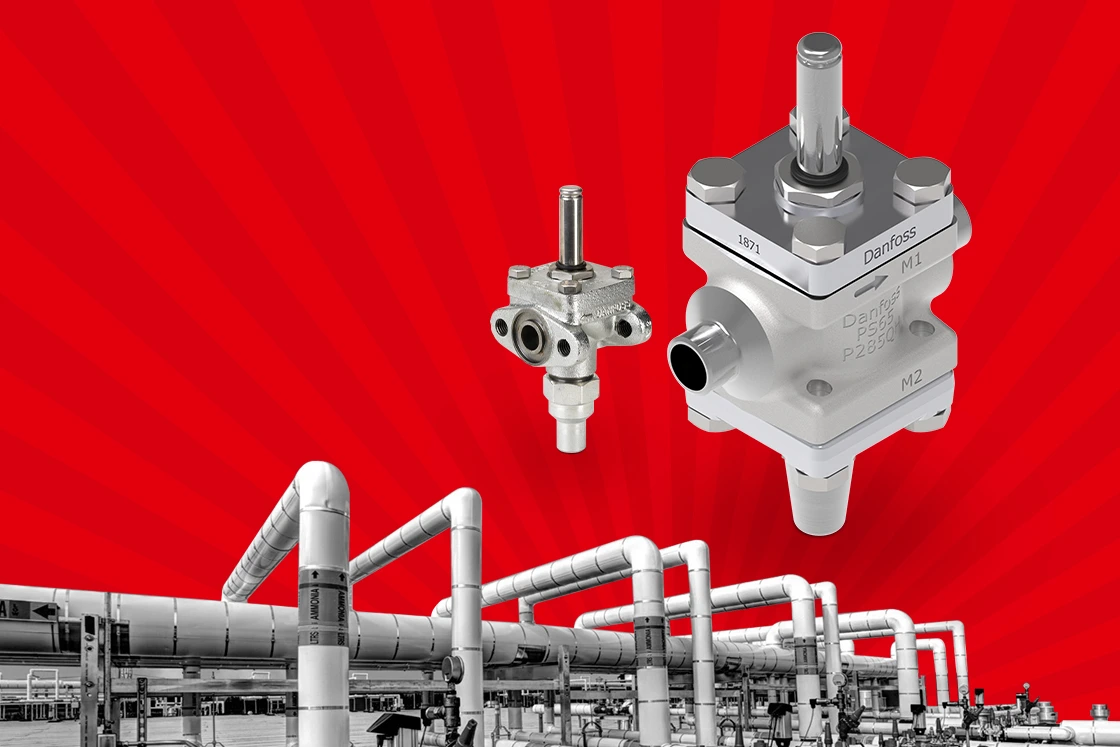
Low Temperature Solenoid Valve for Ammonia Systems the ever-evolving landscape of industrial refrigeration, the need for efficient, reliable components is paramount. One such component that has garnered significant attention is the low temperature solenoid valve specifically designed for ammonia systems. This article explores the functionality, benefits, and applications of these valves, providing insights into why they are essential for modern refrigeration and cooling systems.
Understanding Solenoid Valves
What is a Solenoid Valve?
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical device that controls the flow of fluids. It consists of a coil, a plunger, and a valve body. When an electrical current passes through the coil, it generates a magnetic field that moves the plunger, opening or closing the valve. This simple yet effective mechanism allows for precise control over fluid flow.
Types of Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves come in various types, including:
- Direct Acting: These valves operate directly under the influence of the solenoid and are suitable for low-pressure applications.
- Pilot Operated: These valves use system pressure to open or close, making them suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Two-Way and Three-Way Valves: Two-way valves control the flow between two points, while three-way valves can divert flow between two different paths.
Components of a Solenoid Valve
To understand how low temperature solenoid valves operate, it’s essential to break down their components:
- Coil: The coil is the core element that generates a magnetic field when electricity flows through it.
- Plunger: The plunger is a movable part that responds to the magnetic field created by the coil. It can either open or close the valve.
- Valve Body: The body houses the internal mechanisms and the flow path for the fluid.
- Spring: A spring typically returns the plunger to its default position when the coil is not energized.
Understanding these components helps to appreciate the engineering behind low temperature solenoid valves, especially those designed for ammonia systems.
The Role of Low Temperature Solenoid Valves in Ammonia Systems
Why Ammonia?
Ammonia (NH₃) is widely used as a refrigerant due to its high efficiency and low environmental impact. It has a high latent heat of vaporization, making it ideal for industrial refrigeration applications. However, ammonia poses challenges, particularly at low temperatures, where traditional solenoid valves may fail to operate effectively.
Low Temperature Solenoid Valves
Low temperature solenoid valves are specifically designed to operate efficiently at temperatures below freezing, making them ideal for ammonia systems. These valves are built with materials that can withstand low temperatures and are engineered to prevent issues like freezing or jamming, which can occur with standard valves.
Operating Principles
Low temperature solenoid valves operate on the same basic principles as traditional solenoid valves, but with additional considerations for temperature:
- Material Selection: Materials must be selected to avoid brittleness and failure at low temperatures. Common materials include stainless steel and specially formulated plastics.
- Seal Design: Seals must be designed to prevent leaks while maintaining flexibility at low temperatures.
- Electrical Components: The electrical components must be rated for low-temperature environments to prevent failures.
Understanding these operating principles is essential for engineers and technicians working with ammonia systems, ensuring that they select the right components for their applications.
Key Benefits of Low Temperature Solenoid Valves for Ammonia

1. Enhanced Reliability
Low temperature solenoid valves offer greater reliability in extreme conditions. Their specialized design prevents freezing and ensures smooth operation even in sub-zero environments. This reliability is crucial for industries that depend on continuous refrigeration, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
2. Improved Efficiency
By facilitating precise control over ammonia flow, these valves contribute to overall system efficiency. They minimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs, making them an attractive choice for industrial facilities. Efficient flow control also helps in maintaining optimal temperature settings, further enhancing the efficiency of refrigeration systems.
3. Safety Features
Safety is paramount in any industrial setting. Low temperature solenoid valves often come equipped with fail-safe mechanisms that ensure the system remains operational or safely shuts down in the event of a malfunction. These safety features can prevent catastrophic failures that could result in equipment damage or hazardous situations.
4. Versatility
These valves can be used in a variety of applications, including:
- Refrigeration Systems: For food processing, cold storage, and distribution.
- Industrial Cooling: In manufacturing processes that require precise temperature control.
- HVAC Systems: To regulate temperatures in large buildings or facilities.
- Heat Pumps: In systems that require reversing the flow of refrigerants for heating or cooling.
This versatility makes low temperature solenoid valves a crucial component across multiple industries, showcasing their adaptability to different environments and applications.
Applications of Low Temperature Solenoid Valves
1. Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, maintaining specific temperature ranges is crucial for preserving quality and safety. Low temperature solenoid valves are used in refrigeration systems to control the flow of ammonia, ensuring efficient cooling during storage and transportation. Their reliability helps prevent spoilage, which can lead to significant financial losses.
Case Study: Cold Storage Facilities
Consider a cold storage facility that handles perishable goods. The refrigeration system relies on a low temperature solenoid valve to control ammonia flow. If the valve fails, the temperature can rise quickly, leading to spoilage. By using a specialized low temperature solenoid valve, the facility ensures continuous operation, minimizing risks.
2. Chemical Processing
In chemical processing, ammonia is often used as a refrigerant. Low temperature solenoid valves help maintain the necessary conditions for chemical reactions, enhancing process efficiency and safety. Their ability to operate in extreme temperatures helps ensure that chemical reactions occur under optimal conditions.
Case Study: Ammonia Refrigeration in Chemical Plants
A chemical plant that utilizes ammonia for cooling during reactions benefits from low temperature solenoid valves. These valves enable precise control over the flow of ammonia, ensuring that temperature fluctuations do not disrupt the chemical processes. This reliability contributes to higher yields and safer operations.
3. Ice Rinks and Sports Facilities
Low temperature solenoid valves play a vital role in maintaining the ice surface in rinks. They control the flow of ammonia in cooling systems, ensuring consistent temperatures for optimal ice conditions. This consistency is crucial for sports such as hockey and figure skating, where ice quality directly impacts performance.
Case Study: A Community Ice Rink
A community ice rink relies on a low temperature solenoid valve to regulate ammonia flow. Any malfunction could lead to ice melting or becoming unsafe for skaters. By employing specialized valves, the rink management ensures that ice conditions remain perfect, promoting safety and enjoyment for patrons.
4. Cold Storage Facilities
Cold storage facilities rely on effective refrigeration systems to preserve perishable goods. Low temperature solenoid valves ensure that ammonia flows efficiently, helping maintain the desired low temperatures. This is particularly important for food products that require strict temperature control to prevent spoilage.
Case Study: Temperature Monitoring in Cold Storage
In a large cold storage warehouse, temperature monitoring systems are integrated with low temperature solenoid valves. If temperatures deviate from set points, the system can adjust the ammonia flow through the valves, ensuring that goods are kept at the right temperatures. This proactive approach minimizes waste and enhances inventory management.
5. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The pharmaceutical industry often requires precise temperature control during the manufacturing and storage of drugs. Low temperature solenoid valves help regulate ammonia in refrigeration systems, ensuring that sensitive materials remain within specified temperature ranges. This is crucial for maintaining drug efficacy and compliance with regulatory standards.
Case Study: Vaccine Storage
In vaccine storage facilities, maintaining specific temperatures is vital to ensure the efficacy of vaccines. Low temperature solenoid valves play a crucial role in these systems, allowing for precise control of ammonia flow. By maintaining consistent temperatures, these valves help ensure that vaccines remain effective, safeguarding public health.
6. Data Centers
Data centers generate significant heat due to the operation of numerous servers and electronic components. Low temperature solenoid valves are used in cooling systems to regulate ammonia flow, ensuring that temperatures remain within acceptable limits to protect equipment and data.
Case Study: Optimizing Cooling in Data Centers
A data center employs a cooling system that utilizes low temperature solenoid valves to control ammonia flow. As server loads fluctuate, the valves adjust the cooling output, ensuring that the environment remains optimal. This efficiency not only protects data but also reduces energy costs associated with cooling.
7. Renewable Energy Applications
As the renewable energy sector grows, low temperature solenoid valves are increasingly finding applications in systems like geothermal heat pumps. These valves help regulate the flow of refrigerants in systems designed to harness the earth’s natural heat for heating or cooling buildings.
Case Study: Geothermal Heat Pumps
In a geothermal heating system, low temperature solenoid valves manage the flow of refrigerant through the heat exchanger. This regulation is vital for optimizing the heat transfer process, enhancing system efficiency and reducing energy consumption. As renewable energy becomes more prevalent, the role of these valves in such applications will likely expand.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation is crucial for the effective operation of low temperature solenoid valves. Key considerations include:
- Correct Sizing: Selecting the right size valve is essential for optimal performance. An undersized valve may lead to inadequate flow, while an oversized valve can cause excessive wear.
- Orientation: Follow manufacturer recommendations for valve orientation during installation. Incorrect orientation can lead to operational issues.
- Electrical Connections: Ensure that electrical connections are secure and meet specifications. Poor connections can lead to malfunctions.
- Pipe Compatibility: Ensure that the valve is compatible with the piping materials used in the system to prevent leaks.
- Testing Before Operation: After installation, conduct tests to ensure the valve operates correctly under actual conditions.
Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance helps prolong the life of low temperature solenoid valves. Recommended practices include:
- Routine Inspections: Check for leaks, wear, and proper operation. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they escalate.
- Cleaning: Keep the valve body and surrounding area clean to prevent blockages. Dust and debris can affect valve operation.
- Testing: Periodically test the valve to ensure it opens and closes correctly. This can involve monitoring response times and ensuring that there are no obstructions.
- Lubrication: Where applicable, ensure that moving parts are lubricated to prevent wear and tear.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of maintenance activities and any repairs conducted on the system. This documentation is useful for troubleshooting future issues.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite their reliability, low temperature solenoid valves may encounter issues that require troubleshooting:
- Valve Not Opening/Closing: This may be due to electrical failure or mechanical blockage. Check electrical connections and inspect for debris.
- Leaking Valve: A leaking valve may indicate worn seals or improper installation. Inspect seals and tighten connections as necessary.
- Inconsistent Flow: Fluctuations in flow can result from pressure changes in the system or valve malfunction. Check pressure readings and valve functionality.
- Freezing: If a valve is freezing, it may not be suitable for the temperatures it’s exposed to. Evaluate material compatibility and consider upgrading to a more robust model.
- Noise During Operation: Unusual sounds may indicate wear or failure of internal components. Immediate inspection and possible replacement may be necessary.
Future Trends in Low Temperature Solenoid Valves
Advancements in Materials
As technology progresses, the materials used in low temperature solenoid valves are also evolving. Innovations in polymers and alloys are being developed to enhance performance at extreme temperatures. These materials may offer better durability and resistance to fatigue, further improving reliability.
Smart Materials
The introduction of smart materials that can adapt to temperature changes can enhance valve performance. These materials can provide real-time feedback on operational conditions, allowing for more precise control.
Integration with Smart Technologies
The rise of Industry 4.0 is leading to the integration of smart technologies into industrial components, including low temperature solenoid valves. These advancements can provide real-time monitoring and control, allowing for predictive maintenance and optimization of flow based on dynamic operational conditions.
IoT Integration
Integrating Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities into low temperature solenoid valves can enhance their functionality. IoT-enabled valves can provide data on their operational status, alerting technicians to potential issues before they become serious problems. This capability can lead to significant cost savings through reduced downtime.
Environmental Considerations
With growing awareness of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable solutions in refrigeration is on the rise. Low temperature solenoid valves are being designed with eco-friendly materials and processes to reduce their carbon footprint. Additionally, manufacturers are exploring options for enhanced energy efficiency, contributing to greener industrial practices.
Compliance with Regulations
As regulations surrounding refrigerants and environmental impacts become more stringent, low temperature solenoid valves will likely see adaptations to comply with new standards. This may include modifications to materials used or enhanced safety features to prevent leaks and ensure safe operation.
Automation in Industrial Processes
The push for greater automation in industrial processes is driving innovations in solenoid valve technology. Automated systems that utilize low temperature solenoid valves can operate with minimal human intervention, enhancing efficiency and reliability. This trend is particularly relevant in high-volume production environments where precision and consistency are essential.
The Economic Impact of Low Temperature Solenoid Valves
Cost Savings through Efficiency
Implementing low temperature solenoid valves can lead to significant cost savings for industries. Their efficiency in controlling ammonia flow reduces energy consumption, leading to lower utility bills. Over time, these savings can offset the initial investment in specialized valves.
Return on Investment (ROI)
When considering the ROI of low temperature solenoid valves, it’s essential to factor in both energy savings and the potential reduction in spoilage or product loss due to refrigeration failures. Many facilities find that the upfront costs are quickly recouped through improved efficiency and reliability.
Impact on Productivity
By ensuring consistent temperature control, low temperature solenoid valves contribute to overall productivity in industrial settings. They help maintain optimal conditions for processes that depend on precise temperature regulation, reducing downtime and enhancing throughput.
Job Creation and Skills Development
As industries adopt more advanced technologies, including low temperature solenoid valves, there will be a corresponding need for skilled technicians and engineers. This demand can drive job creation and promote skills development within the workforce, particularly in fields related to automation, refrigeration, and system maintenance.
Conclusion
Low temperature solenoid valves for ammonia systems are essential components in various industrial applications, from food processing to chemical manufacturing. Their reliability, efficiency, and safety features make them indispensable in maintaining optimal operational conditions. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and sustainability, the role of these specialized valves will only grow, ensuring that systems operate smoothly and safely even in the most demanding environments.
By understanding the functionality and advantages of low temperature solenoid valves, industries can make informed decisions that enhance their refrigeration systems and contribute to overall operational excellence. As technology advances, these valves will likely continue to evolve, integrating even more sophisticated features that enhance performance and reliability in ammonia systems.
The future of low temperature solenoid valves is bright, with ongoing innovations paving the way for even more efficient and reliable solutions in the world of industrial refrigeration. By investing in these advanced technologies, industries can ensure not only the longevity of their systems but also their commitment to sustainable and efficient operations.
This comprehensive exploration of low temperature solenoid valves highlights their significance in modern industrial applications. As we move forward, staying informed about these technologies will be crucial for industries looking to enhance efficiency, safety, and sustainability in their operations.for more details please visit the website networksights.com











Leave a Reply